The histogram function from plotly
Histograms are used to represent the distribution of a numerical variable. When using plotly, the histogram function from plotly express allows creating this type of charts in an easy way. You will need to input your variable to the x argument for a vertical histogram. The data can also be a column of a pandas data frame. By default, the function will create a frequency histogram.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(5)
fig = px.histogram(x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100))
# Alternative: data from a pandas data frame column
# import pandas as pd
# df = pd.DataFrame({'x': np.random.normal(0, 1, 100)})
# Histogram from data frame
# fig = px.histogram(df, x = "x")
fig.show()Horizontal histogram
If you want to create a horizontal histogram instead of vertical you just need to input your data to y instead of to x.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(5)
fig = px.histogram(y = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100))
fig.show()Density histogram
The default histogram created with histogram is a frequency histogram. However, you can set the histnorm argument to 'probability density' in order to create a density histogram. Other possible values are 'percent', 'probability' and 'density'.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(5)
fig = px.histogram(x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
histnorm = 'probability density')
fig.show()Title and axis labels
You can add a title to the chart with title and customize the default axis labels passing a dict to labels, as shown below.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(5)
fig = px.histogram(x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
title = 'Histogram of x',
labels = {'x': 'X-axis', 'y': 'Y-axis'})
fig.show()Number of bins
The number of bins of the histogram is selected automatically based on the input data, but you can set the number you want with nbins.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(5)
fig = px.histogram(x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100), nbins = 50)
fig.show()Labels
The histogram function also provides an argument named text_auto which adds the count for each bin when set to True.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(5)
fig = px.histogram(x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100), text_auto = True)
fig.show()Histogram color
The color of the bins can be customized through the color_discrete_sequence argument. In addition, the opacity argument controls the transparency of the color.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(5)
fig = px.histogram(x = np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
color_discrete_sequence = ['firebrick'],
opacity = 0.5)
fig.show()Histogram by group
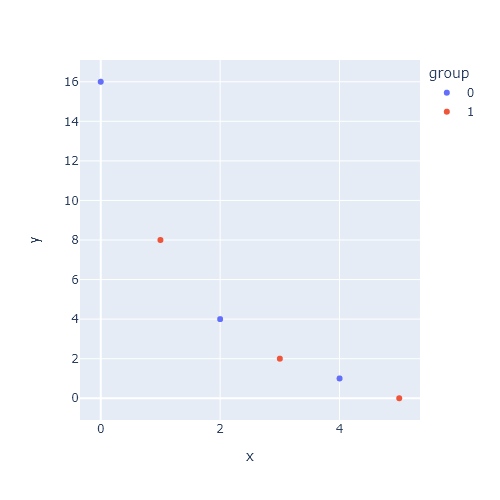
Relative (default)
Passing a categorical variable representing groups to color you will be able to create a histogram by group. The method used by default is called 'relative', where bars are stacked above zero for positive values and below zero for negative values.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(5)
df = pd.DataFrame({'x': np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
'group': np.repeat(np.array(["G1", "G2"]), [50, 50], axis = 0)})
fig = px.histogram(df, x = 'x', color = 'group')
fig.show()Note that you can use the color_discrete_map or color_discrete_sequence arguments to customize the color of the bins for each group.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(5)
df = pd.DataFrame({'x': np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
'group': np.repeat(np.array(["G1", "G2"]), [50, 50], axis = 0)})
fig = px.histogram(df, x = 'x', color = 'group',
color_discrete_map = {'G1': 'green', 'G2': 'orange'})
fig.show()Overlay
The default method can be customized with the barmode argument. When set to 'overlay' the groups will overlay.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(5)
df = pd.DataFrame({'x': np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
'group': np.repeat(np.array(["G1", "G2"]), [50, 50], axis = 0)})
fig = px.histogram(df, x = 'x', color = 'group', barmode = 'overlay')
fig.show()Group
The group method will place the bars beside each other.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(5)
df = pd.DataFrame({'x': np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
'group': np.repeat(np.array(["G1", "G2"]), [50, 50], axis = 0)})
fig = px.histogram(df, x = 'x', color = 'group', barmode = 'group')
fig.show()Stack
The last available method is stack, which will stack the values for the different groups.
import plotly.express as px
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
np.random.seed(5)
df = pd.DataFrame({'x': np.random.normal(0, 1, 100),
'group': np.repeat(np.array(["G1", "G2"]), [50, 50], axis = 0)})
fig = px.histogram(df, x = 'x', color = 'group', barmode = 'stack')
fig.show()